
寫程式應該很常會用到指數運算,過去我們會用 Math.pow(),但在 ES2016 (ES7) 提供了 exponentiation operator (指數運算子) 的讓寫法更簡潔。那這兩個差在哪?讓我們從 ECMAScript spec 中一探究竟吧。
本文同步發表於 Titangene Blog:JavaScript 之旅 (3):Exponentiation Operator (指數運算子)
「JavaScript 之旅」系列文章發文於:
Math.pow()過去要進行指數運算 (即計算 a 的 n 次方,表達式為 $a^n$,a 為底數,n 為指數,通常指數寫成上標,放在底數的右邊),常用的是 Math.pow() (應該不會想手動寫多個 * 運算子 (multiplicative operators) 吧?)。例如:
平方:
let x = 2;
console.log(Math.pow(x, 2)); // 4
// 等同於
console.log(x * x); // 4
三次方:
let x = 2;
console.log(Math.pow(x, 3)); // 8
// 等同於
console.log(x * x * x); // 8
寫成函數可能像是這樣:
let square = x => Math.pow(x, 2);
let cube = x => Math.pow(x, 3);
console.log(square(6)); // 36
console.log(cube(3)); // 27
在 ES2016 (ES7) 提供了 exponentiation operator (指數運算子),用於指數運算。
exponentiation 運算子是一種 infix notation (中綴表示法),比用函數表示法還要更簡潔。
let square = x => x ** 2;
let cube = x => x ** 3;
註:有些程式語言會用
^運算子來進行指數計算,但 JavaScript 的^運算子是 bitwise XOR 運算子,用來進行位元運算,例如:let a = 5; // 00000000000000000000000000000101 let b = 3; // 00000000000000000000000000000011 console.log(a ^ b); // 00000000000000000000000000000110
若與 NaN 計算,結果都會是 NaN:
console.log(NaN ** 2); // NaN
console.log(2 ** NaN); // NaN
若與 undefined 計畫,結果也都會是 NaN:
console.log(undefined ** 2); // NaN
console.log(2 ** undefined); // NaN
因為 exponentiation 運算子會將指數和底數值進行
ToNumeric()強制轉型,很像使用Number()的行為,如果你嘗試用Number(undefined)會得到NaN。後面會提到 spec 是如何定義的。
若與 null 計算,null 會被 ToNumeric() 強制轉型成 0:
console.log(null ** 2); // 0
// 大約等同於 Number(null) ** 2,所以 0 ** 2 的計算結果為 0
console.log(2 ** null); // 1
// 大約等同於 2 ** Number(null),所以 2 ** 0 的計算結果為 1
exponentiation 運算子的 associativity 是右到左 (即 right-associative),也就是說,下面兩個寫法是相同的:
console.log(2 ** 3 ** 2); // 512
console.log(2 ** (3 ** 2)); // 512
// 計算過程:
// 1. 2 ** 3 ** 2
// 2. 2 ** 9
// 3. 512
所以會與下面的計算結果不同,因為你讓他先計算括號的結果:
console.log((2 ** 3) ** 2); // 64
// 計算過程:
// 1. (2 ** 3) ** 2
// 2. 8 ** 2
// 3. 64
後面會說 spec 是如何定義的。
註:在程式語言中,operator associativity 是在沒有括號時,如何將有相同優先級的運算子進行分組,運算元要用哪種運算會取決於運算子的 associativity。
分為以下幾種:
- associative:可任意分組運算子
- left-associative:運算子從左側分組
- right-associative:運算子從右側分組
- non-associative:運算子不能 chained,通常是因為 output typ 和 input type 不相容
不過,exponentiation 運算子不能讓你在底數前面使用 unary operation (一元運算子,包括 +、-、~、!、delete、void 和 typeof ),否則會出現 SyntaxError 錯誤,所以以下都會是 SyntaxError。
let a = 2;
let n = 3;
console.log(+a ** n);
console.log(-a ** n);
console.log(~a ** n);
console.log(!a ** n);
delete a ** n;
void a ** n;
typeof a ** n;
// SyntaxError: Unary operator used immediately before exponentiation expression. Parenthesis must be used to disambiguate operator precedence
例如:要把負數當作底數就不能像下面這樣直接寫負號:
let a = 2;
let n = 3;
console.log(-2 ** 3);
console.log(-a ** n);
// SyntaxError: Unary operator used immediately before exponentiation expression. Parenthesis must be used to disambiguate operator precedence
上面是 Chrome 的錯誤訊息,已經提醒你要加上括號。
而是要加上括號才能計算:
console.log((-2) ** 3); // -8
另一個範例:想將指數計算結果變為負數,也需要用括號:
console.log(-(2 ** 10)); // -1024
exponentiation 運算子也有 assignment operator (賦值運算子),語法是 **=。
例如:
let x = 2;
x **= 3;
console.log(x); // 8
等同於:
let x = 2;
x = x ** 3;
console.log(x); // 8
Math.pow()共通點:都可以計算幾次方
但有一些不同:exponentiation 運算子可以計算 BigInt 型別的值,但 Math.pow() 不行
console.log(2n ** 3n); // 8n
console.log(Math.pow(2n, 3n)); // TypeError: Cannot convert a BigInt value to a number
exponentiation 運算子是 ECMAScript 內建 Numeric 型別 (Number 和 BigInt 型別都是 Numeric 型別) 的 operation:
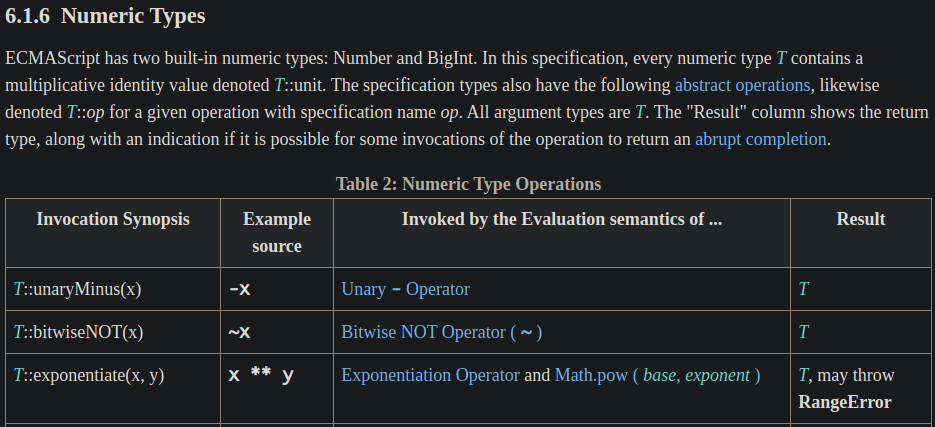
下面是 Number::exponentiate operation 的定義:
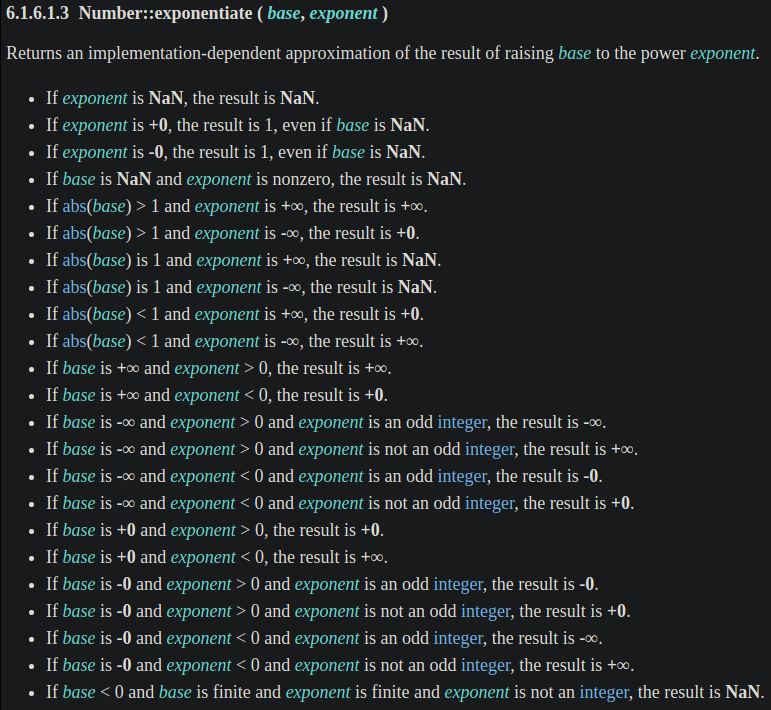
下面是 BigInt::exponentiate operation 的定義:

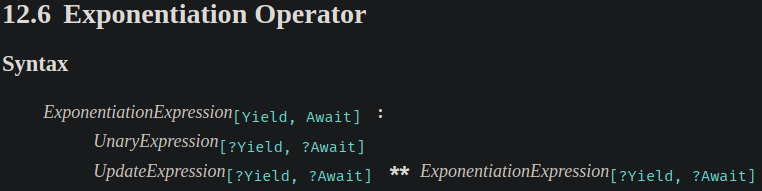
接著從 spec 定義的語法可以看出,exponentiation 運算子的 associativity 是右到左 (即 right-associative):
下面是 spec 定義 exponentiation 運算子的計算過程:
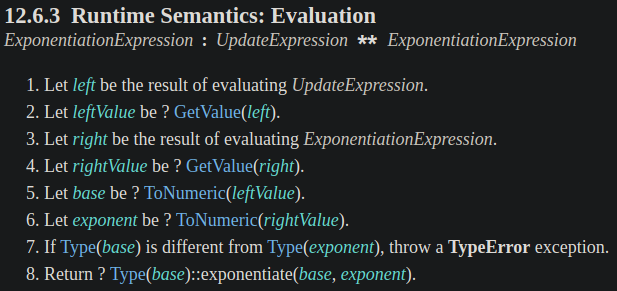
從步驟 5 和 6 可以看到,exponentiation 運算子會把底數和指數進行 ToNumeric() 的強制轉型。
若我故意讓底數和指數是 String 型別的值時,exponentiation 運算子就會自動幫我強制轉型成 Number 型別:
console.log('2' ** '3'); // 8
下面是 ToNumeric() 的定義:

至於
ToNumeric()在定義中提到的ToPrimitive()和ToNumber()是 ECMAScript 強制轉型的定義了,這邊不會深入探討,有興趣的朋友可以看看,我有附上連結。
若以簡化的方式來說,我們常用的 Number() constructor 的其中一個步驟就會使用到 spec 中定義的 ToNumeric():

註:不知道看到這邊會不會亂掉 XD,有些是 spec 中定義的,我們是無法透過寫程式直接使用的,例如:
ToNumeric()、ToPrimitive()、ToNumber()都是。而
Number()才是我們真的可以使用的 constructor。所以不要搞混囉!
Math.pow() 的 spec 定義接著來看 Math.pow() 在 spec 的定義:

可以看到 Math.pow() 和 exponentiation 運算子對底數和指數值的處理不同:
Math.pow() 是進行 ToNumber() 的強制轉型ToNumeric() 的強制轉型